印度墨水灌注法重建小鼠全脑连续血管网
染色方法:
印度墨水染色
标记方法:
印度墨水心脏灌注
包埋方法:
树脂包埋
成像平台:
BioMapping 5000

cover
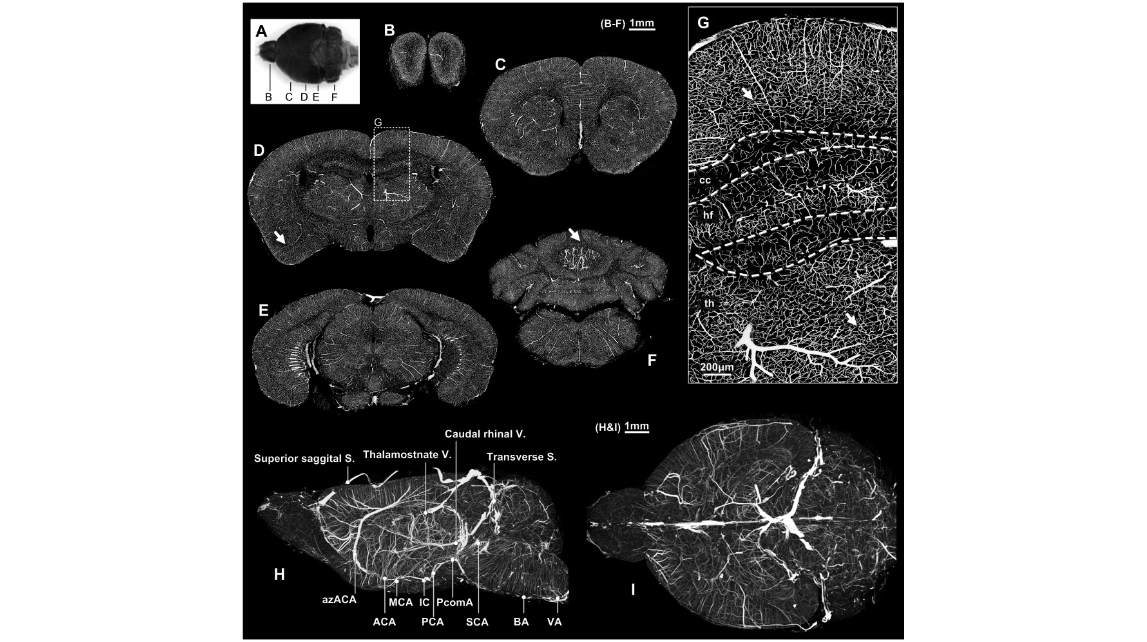
Figure 1. Vessel acquisition and reconstruction in the whole mouse brain. A: The dorsal view of the gelatin-Indian ink perfused brain; after embedding with Spurr resin and imaging using MOST to acquire the three-dimensional cerebrovascular dataset, five 100- m m thick coronal planes were selected and MIP-reconstructed in the olfactory bulb (B), frontal (C), hippocampus (D), midbrain (E) and cerebellum (F); the results showed desirable perfusion in the whole brain, and no blank areas were found in the brain entity. G: ROI in Figure 1D; the capillary network was continuous, and no gaps were found. H: The left view of the whole brain; several major vessels were marked. I: The top view of the whole brain. cc: corpus callosum; hf: hippocampus; th: thalamus. B–F: Bar=1 mm; G: Bar=200 m m, H: Bar=1 mm.
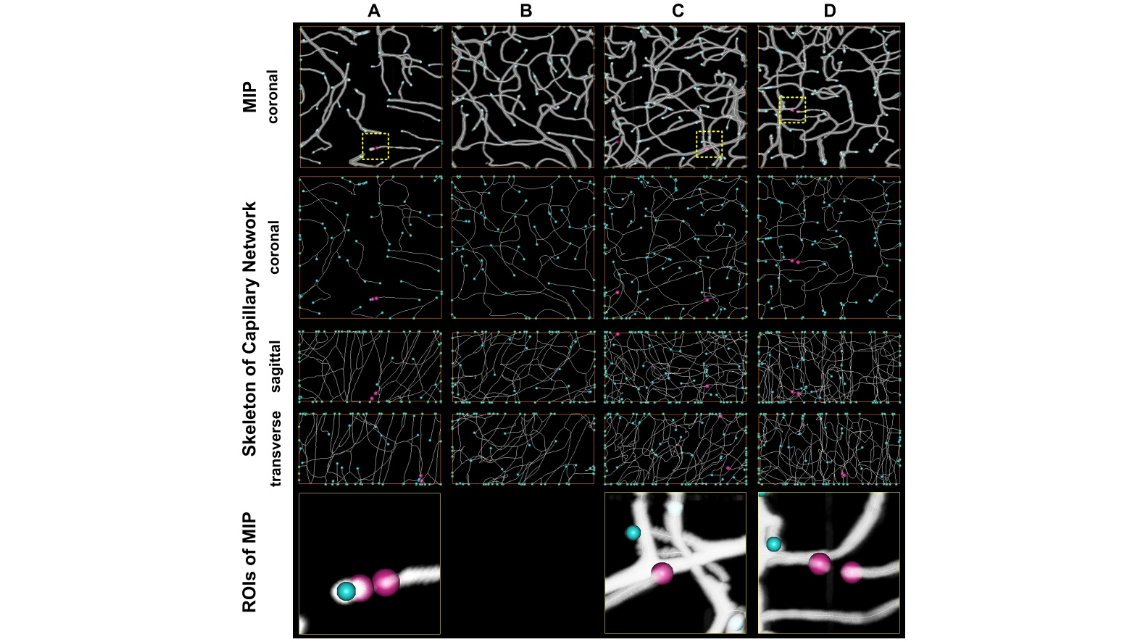
Figure 2. Assessment of capillary continuity. Four ROIs (Columns A–D) with size of 20062006100 m m 3 at cortex, amygdaloid nucleus, thalamus, cerebellar lobule were selected and used to analyze the vascular continuity. The four ROIs were indicated sequentially with white arrows in Figure 1D, F and G. ROI A was taken as an example. On the top row, the MIP reconstruction of this ROI covered with vascular tracking results by using Amira was shown. The vascular terminal could be located through vascular tracking results projection on xy, yz and xz orthogonal planes (Rows 2–4). The vascular terminals inside the ROI were marked with red balls, while the terminals on the boundary were marked with blue balls. The panels on the bottom showed the details around the vascular terminals, most of which were caused by caliber narrowing.
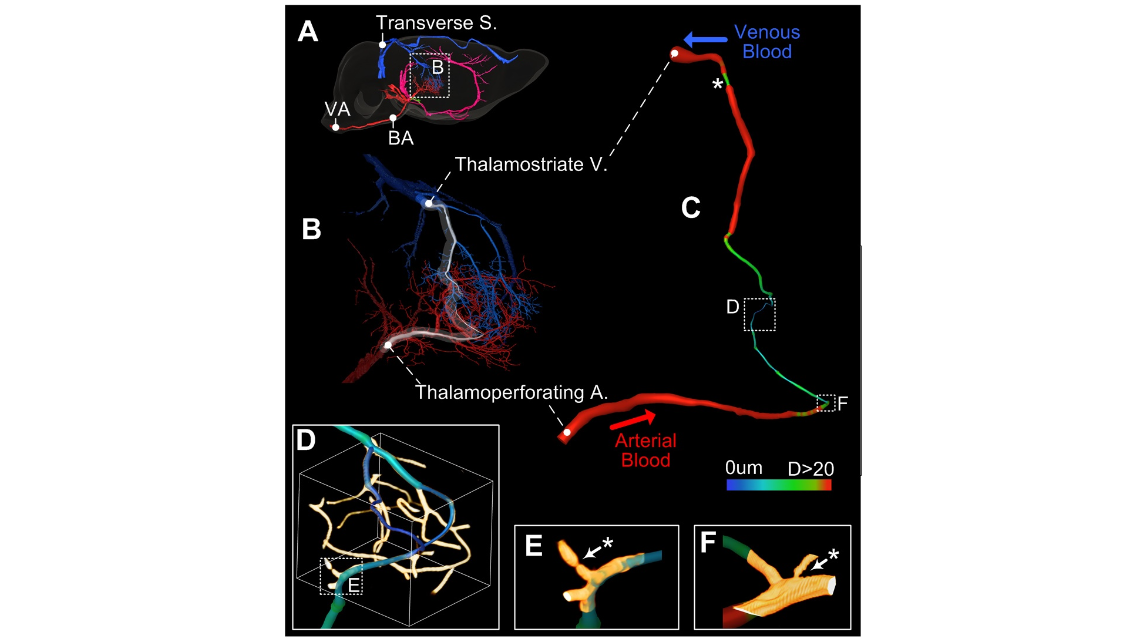
Figure 3. Blood supply pathway tracking and analysis in the right thalamus. A: The right view of the brain. A clear blood pathway begins in the VA, passes through the BA and the thalamoperforating artery, enters the thalamus, and finally drains out through the thalamostriate vein, the great cerebral vein of Galen and the transverse sinus. B: The vessels with diameters larger than 5 m m in the thalamus, red for arteries and blue for veins. C: A vascular segment from the thalamoperforating artery to the thalamostriate vein through the capillary, colored by diameter. D: The capillaries in the pathway from the artery to the vein. E–F: ROIs from D and C, showing the narrowing in the capillaries. * Identifies the vascular narrowing sites in C, E and F.
Video S1 Blood supply pathway tracking in the thalamus.
Video S2 Slices appear in a sequential way to show 100 um MIP reconstructions on coronal plane for the whole brain.
Video S3 Slices appear in a sequential way to show 100 um MIP reconstructions on sagittal plane for the whole brain.

cover

Figure 1. Vessel acquisition and reconstruction in the whole mouse brain. A: The dorsal view of the gelatin-Indian ink perfused brain; after embedding with Spurr resin and imaging using MOST to acquire the three-dimensional cerebrovascular dataset, five 100- m m thick coronal planes were selected and MIP-reconstructed in the olfactory bulb (B), frontal (C), hippocampus (D), midbrain (E) and cerebellum (F); the results showed desirable perfusion in the whole brain, and no blank areas were found in the brain entity. G: ROI in Figure 1D; the capillary network was continuous, and no gaps were found. H: The left view of the whole brain; several major vessels were marked. I: The top view of the whole brain. cc: corpus callosum; hf: hippocampus; th: thalamus. B–F: Bar=1 mm; G: Bar=200 m m, H: Bar=1 mm.

Figure 2. Assessment of capillary continuity. Four ROIs (Columns A–D) with size of 20062006100 m m 3 at cortex, amygdaloid nucleus, thalamus, cerebellar lobule were selected and used to analyze the vascular continuity. The four ROIs were indicated sequentially with white arrows in Figure 1D, F and G. ROI A was taken as an example. On the top row, the MIP reconstruction of this ROI covered with vascular tracking results by using Amira was shown. The vascular terminal could be located through vascular tracking results projection on xy, yz and xz orthogonal planes (Rows 2–4). The vascular terminals inside the ROI were marked with red balls, while the terminals on the boundary were marked with blue balls. The panels on the bottom showed the details around the vascular terminals, most of which were caused by caliber narrowing.

Figure 3. Blood supply pathway tracking and analysis in the right thalamus. A: The right view of the brain. A clear blood pathway begins in the VA, passes through the BA and the thalamoperforating artery, enters the thalamus, and finally drains out through the thalamostriate vein, the great cerebral vein of Galen and the transverse sinus. B: The vessels with diameters larger than 5 m m in the thalamus, red for arteries and blue for veins. C: A vascular segment from the thalamoperforating artery to the thalamostriate vein through the capillary, colored by diameter. D: The capillaries in the pathway from the artery to the vein. E–F: ROIs from D and C, showing the narrowing in the capillaries. * Identifies the vascular narrowing sites in C, E and F.
Video S1 Blood supply pathway tracking in the thalamus.
Video S2 Slices appear in a sequential way to show 100 um MIP reconstructions on coronal plane for the whole brain.
Video S3 Slices appear in a sequential way to show 100 um MIP reconstructions on sagittal plane for the whole brain.
2014年1月30日,华中科技大学武汉光电国家研究中心李安安教授实验组,使用MOST技术,结合改进的明胶-印度墨汁血管灌注,展示了小鼠全脑血管网络成像。本研究为同时研究小鼠脑的整个宏观和微观血管网络提供了一种有效的方法。文章发表在《PLoS One》杂志上。
参考文献
参考文献[1]:Xue S, Gong H, Jiang T, Luo W, Meng Y, Liu Q, Chen S, Li A. Indian-ink perfusion based method for reconstructing continuous vascular networks in whole mouse brain. PLoS One (2014);9(1):e88067.

